TODAY IN FOCUSSupport
Energy Transition
Sustainable energy future depends on new infrastructure development and equipment, requiring even more energy during the transition phase.
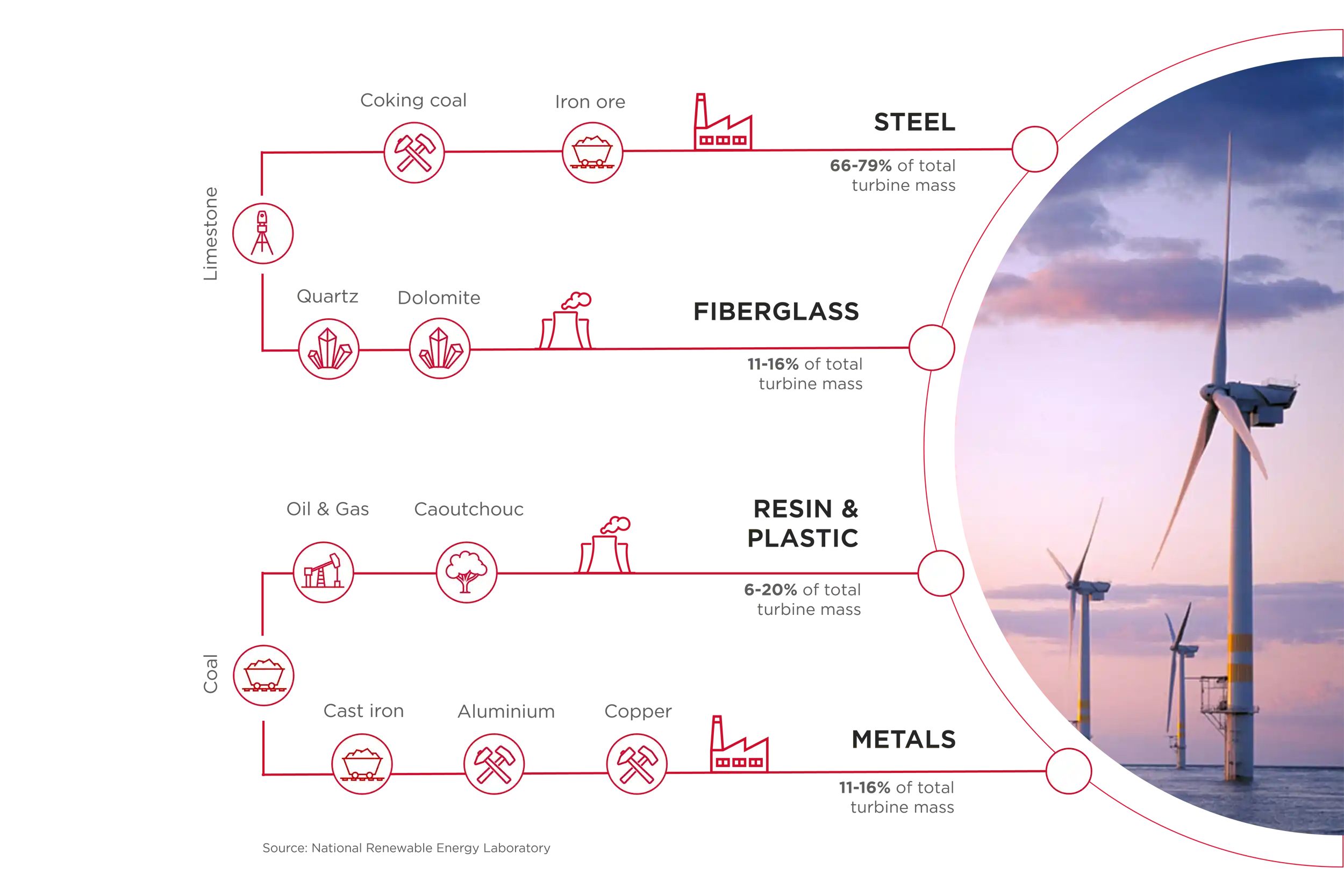
The existing energy landscape relies heavily on large-scale extraction of fossil fuels and intricate supply chains for transportation and distribution. As an example – coal, being gradually replaced in some countries for power generation,
continues to play a crucial role in iron and steel production until newer technologies are available.
Recent global energy crises, fuelled by geopolitical conflicts, have highlighted the importance of uninterrupted and affordable energy supply for economies, households, and industries.

of global electricity
Coal still supplies just over a third of global electricity generation
of the world's steel production
Coal and coke are still indispensable sources of energy and carbon for the steelmaking process
times
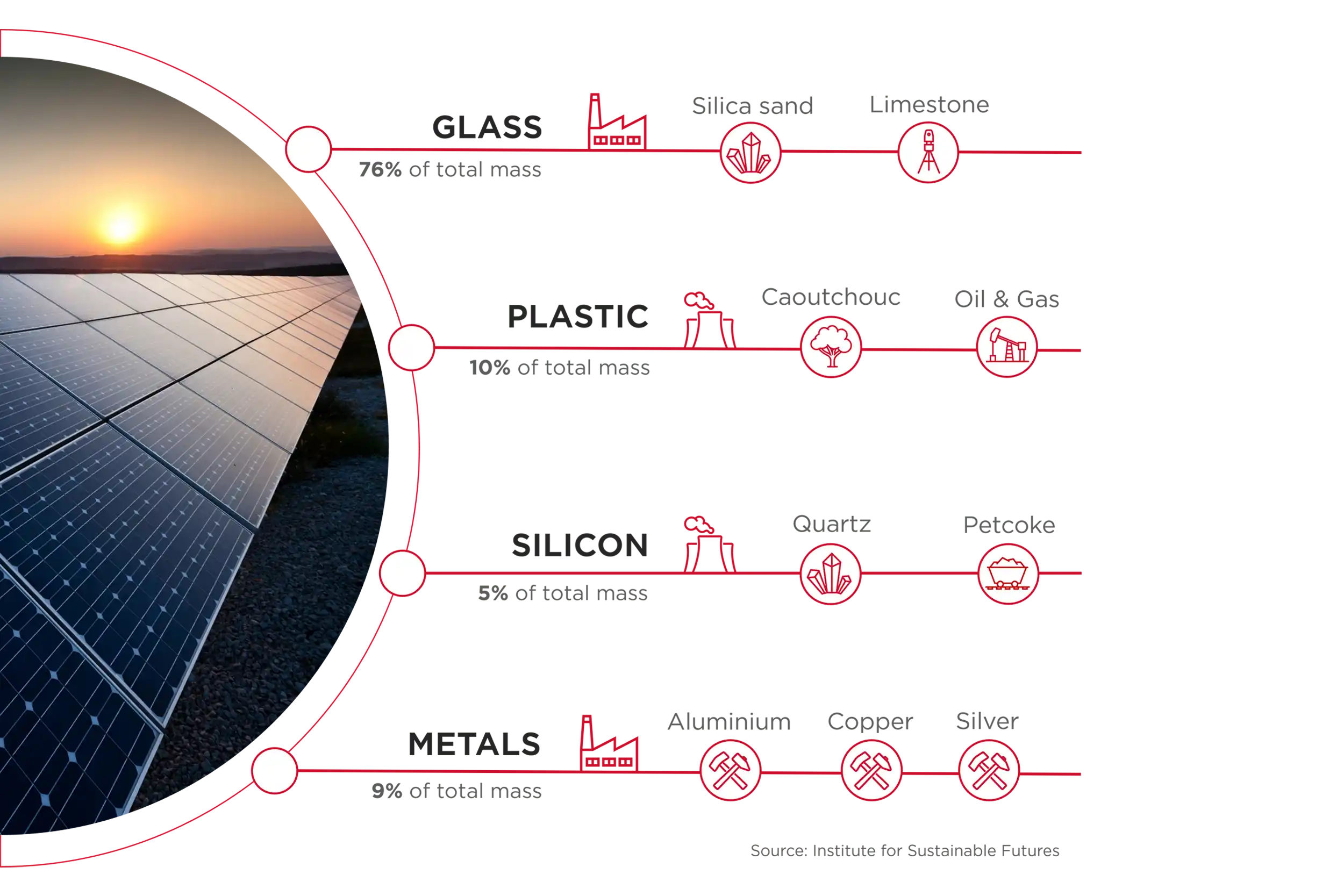
Demand for minerals used in clean energy will raise from 6 to 40 times by 2040 relative to 2020

Energy Transition
Main problem