Corn, also known as maize, is the top produced and one of the most widely consumed crops globally, plays a significant role in the agricultural sector of many countries. It serves not only as a diet for billions but also as a critical raw material in industries from livestock feed to biofuels.
A single corn cob, on average, has an even number of rows, usually 16. This symmetry is one of the fascinating genetic consistencies found in nature.
Originating from ancient Mesoamerica over 9,000 years ago, corn has evolved significantly due to selective breeding by indigenous peoples. It spread across the Americas before making its way to Europe in the 15th and 16th centuries, following the voyages of European explorers. Today, it is cultivated on every continent except Antarctica.
Unlike many other crops, corn cannot survive in the wild without human intervention. Its seeds are packed tightly together and covered by a tough husk, which prevents natural dispersal.
Production landscape
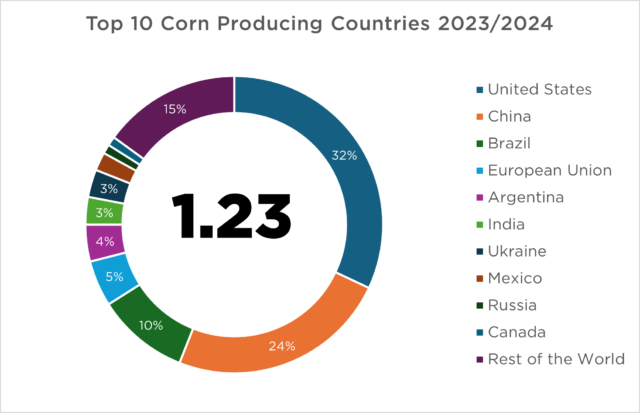
In 2023-2024, global corn production is witnessing record highs, propelled by favorable weather conditions and technological advancements in agriculture. The United States leads global corn production with 32% of the total volumes, followed by China, Brazil, and Argentina. The Midwest region, often referred to as the Corn Belt, is the heart of U.S. corn farming.
Notably, Brazil’s corn output is expected to reach unprecedented levels due to conducive weather patterns that have enhanced yield prospects. This increase is a significant component of the broader surge in global coarse grains production, which is estimated at 1.53 billion tonnes.
About 60% of corn produced worldwide is used as animal feed, with the remainder used for ethanol, corn syrup, and as a human food product.
Data Source: US Department of Agriculture
Major contributors
The international corn market is experiencing robust activity, with trade volumes anticipated to expand further. The total trade in coarse grains, including corn, for 2023/24 is forecasted to rise by 1.1 million tonnes. This increment is primarily driven by heightened demand in China, projecting the global coarse grain trade at about 236 million tonnes, a 4.9% increase from the previous year.
In 2023/24, Brazil has become a leading exporter with 56 million metric tons, mainly delivering corn to China and the European Union. However, the United States remains the largest player in the market with 46 million tons, distributing corn globally to destinations such as Mexico, Japan, and South Korea. Next, Argentina and Ukraine contribute notable volumes, exporting 32 million metric tons and 21 million metric tons, respectively. Argentina’s exports are mainly directed towards Southeast Asia and the Middle East, while Ukraine focuses on the European and Chinese markets. Summing up, these countries make around 85% of global corn production volumes.
Who Imports the Most?
In 2023, the landscape of global corn importation showcases some familiar faces leading the charge. China tops the list importing over 23 mln, with an $5.76 billion spent on imports in just the first three quarters of the year. Increased demand is driven by China’s growing population and its escalating needs for animal feed and biofuels, making imports a critical supplement to its domestic production.
Not far behind, Japan secures the position as one of the world’s most significant importers at $3.82 billion. Japanese markets primarily use maize for animal feed and to support a vast food processing industry that demands consistent and reliable corn supplies. Mexico, with its deep-rooted culinary traditions that heavily rely on corn, spent $3.43 billion to meet substantial domestic needs, especially for cuisine and animal feed sectors.
South Korea also makes a significant entry into the top importers, channeling $2.65 billion into corn imports to fuel its extensive livestock industry and for various industrial purposes, including cornstarch and ethanol production. Lastly, Spain, with its significant demand for both plant and animal feed due to a large agricultural base, imported corn for $1.90 billion.
Will demand for corn continue to grow?
Coming to its application, maize is not only a food and feed crop but also a key component in production of biodegradable plastics, adhesives, sweeteners like high-fructose corn syrup and biofuels, particularly ethanol. The Renewable Fuel Standard policy in the U.S. mandates the blending of ethanol with gasoline, boosting corn demand. Ethanol produced in this way accounts for about 10% of the U.S. gasoline market. Ethanol is blended with gasoline to produce a more environmentally friendly fuel that burns cleaner than gasoline alone.
Moreover, the byproducts of corn are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and paper manufacturing.
While 10-year CAGR is only 1-2%, 2023-2024 increase stands around 6%.
This diversification in use cases underscores corn’s integral role in both food and industrial sectors. Additionally, the cultural significance of corn spans many civilizations, where it has been a staple crop and a symbol of life and fertility, especially in the Americas, where it originally comes from.
Future Opportunities
The global corn market continues to show strength and resilience, with record production levels and rising trade volumes highlighting its critical importance. As environmental and economic factors evolve, the ability of major producers to adapt will significantly impact global food security and economic stability. Looking forward, the corn industry is poised to remain a cornerstone of global agriculture, driving innovations and supporting millions of livelihoods worldwide. At Maxwer, we continue to supply essential commodities to different destinations, creating sustainable supply chains together with our partners.