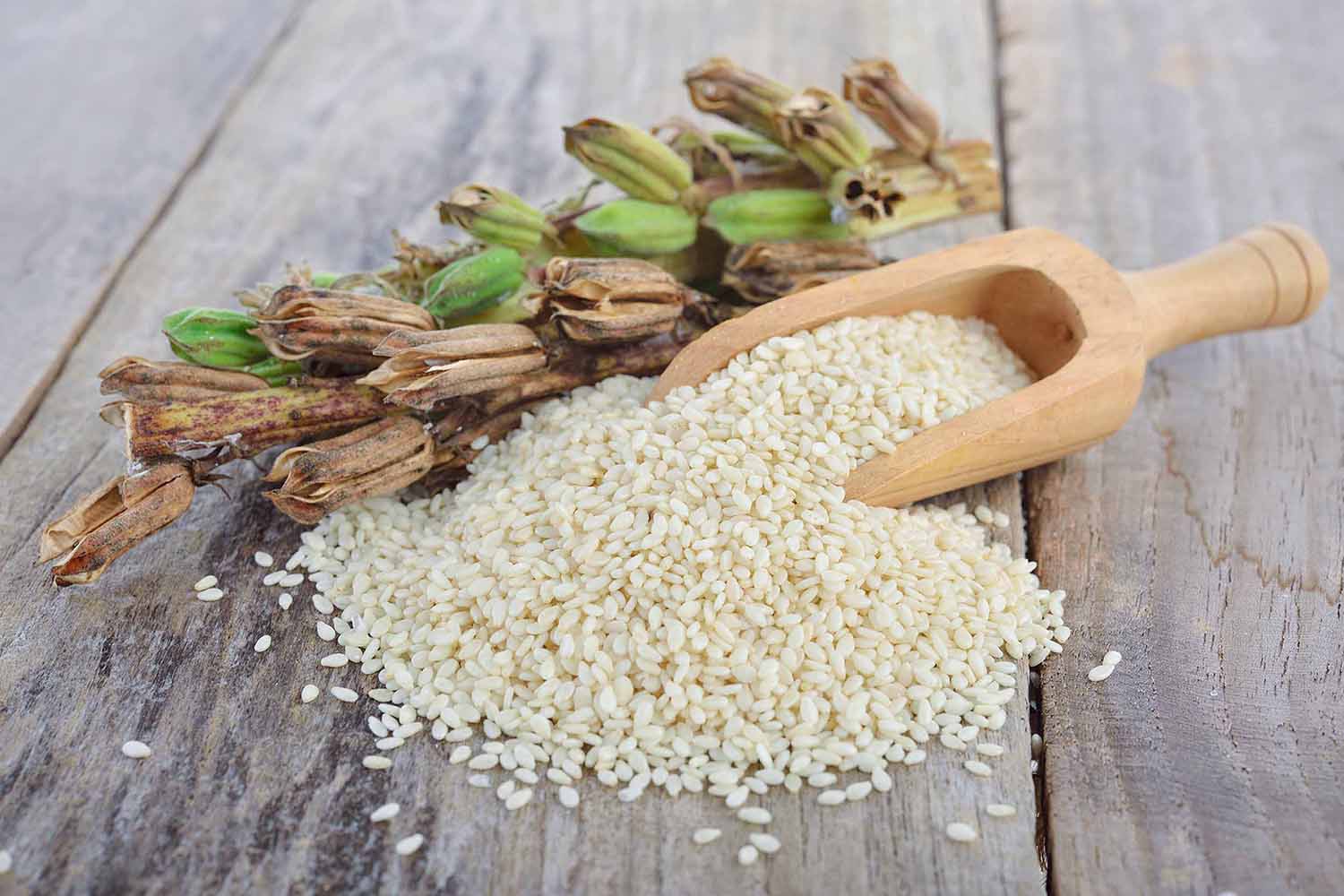
Sesame seeds, a tiny powerhouse of nutrition and flavor, have been an integral part of global culinary traditions for centuries. Not only are they a versatile ingredient, but they also serve as a valuable agricultural commodity.
Did you know that sesame seeds have a rich history dating back thousands of years? They are believed to be one of the oldest oilseed crops cultivated by humans. Evidence of sesame seed usage can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians, Assyrians, and Egyptians, who valued the seeds for their flavor, oil, and medicinal properties.
The world trade of sesame seeds has experienced substantial growth in recent years, as demand for this nutritious ingredient continues to rise. Let’s delve to the world of sesame seeds trading, including production hubs, major players, the factors contributing to its global popularity and certainly how it’s connected with world-famous Sesame Street.
Production Hubs and Major Producers
Sesame seeds are primarily cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The largest producers of sesame seeds include countries such as India, China, Myanmar, Sudan, Tanzania and Ethiopia. These nations benefit from suitable climatic conditions and have a long history of sesame seed cultivation. Each country brings its unique varieties and qualities to the global market, resulting in diverse choices for consumers and businesses.
The world’s total production of sesame seeds is estimated to be around 8-9 million metric tons annually and it’s continuing to grow.
Sesame Trading Landscape
The global trade of sesame seeds has witnessed a significant increase over the years due to growing demand from both traditional and emerging markets. Asia, particularly India and China, remains the dominant region for sesame seed consumption and trade. These countries not only produce substantial amounts of sesame seeds but also have a well-established domestic market. Additionally, they export significant quantities to cater to international demand.
Other regions, such as the Middle East, Africa, and Europe, are also significant players in the sesame seed trade. Middle Eastern countries like Turkey and Israel have a long-standing tradition of incorporating sesame seeds in their cuisine, making them important importers.
From other hand, Asian countries, particularly India, China, and Japan, represents a major portion of global sesame seed consumption. At the same time, North American region has the highest growth rate in Sesame Seeds Market. The exact figures for consumption volumes can vary, but it is estimated that these countries have substantial domestic demand due to their culinary traditions and usage in various dishes.
Factors Driving Global Sesame Boom
The rising global popularity of sesame seeds can be attributed to its nutritional value, culinary versatility, and increasing consumer awareness. Despite their small size, sesame seeds pack a nutritional punch. They are an excellent source of healthy fats, protein, dietary fiber, and essential minerals such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. Incorporating sesame seeds, loaded with potent amino acids, such as tryptophan and polyphenols, into your diet can contribute to overall health and well-being as well as help reduce weight.
Moreover, sesame seeds’ versatility adds to their appeal. They are used in various forms, including whole seeds, oils, pastes (such as tahini), and flour. Sesame oil, with its distinctive flavor and high smoke point, is particularly sought after for cooking and culinary applications. The popularity of international cuisines, such as Middle Eastern, Asian, and Mediterranean, has also contributed to the surge in sesame seed demand worldwide.
Sesame seeds hold symbolic significance in various cultures. In ancient Greek mythology, sesame seeds were associated with the goddess Demeter and were believed to possess mystical powers. In some Asian cultures, sesame seeds are considered a symbol of immortality, longevity, and abundance.
Moreover, Sesame seeds are known for their high oil content, which ranges from 40% to 60%. This characteristic makes sesame oil a valuable cooking and flavoring ingredient, as well as a sought-after component in cosmetics, soaps, and skincare products.
Good to know that the popular children’s television show Sesame Street named exactly after the sesame seed, known for its ability to open up and reveal hidden treasures, mirroring the show’s aim to educate and entertain children while uncovering new learning opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the global sesame seed trade presents lucrative opportunities, it is not without challenges. Climate change and unpredictable weather patterns pose a threat to sesame seed production in several regions. Droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures can impact crop yields and quality. Additionally, factors like pest infestations and disease outbreaks can affect production and supply.
However, these challenges have opened doors for innovation and sustainable practices in the sesame seed industry. Farmers and agricultural researchers are exploring drought-resistant varieties, implementing efficient irrigation techniques, and adopting organic farming methods to mitigate the environmental impact. This focus on sustainability aligns with the increasing demand for responsibly sourced and organic food products.
While Asian countries remain major producers and consumers, other regions like the Middle East, Africa, Europe and North America are also actively involved in the sesame seed trade. As the popularity of sesame seeds continues to rise globally, the trade dynamics are expected to evolve further, presenting both opportunities and challenges. We at Maxwer will keep our focus on supporting agricultural producers and traders all over the world contributing to the steady growth of sustainable supply chains.